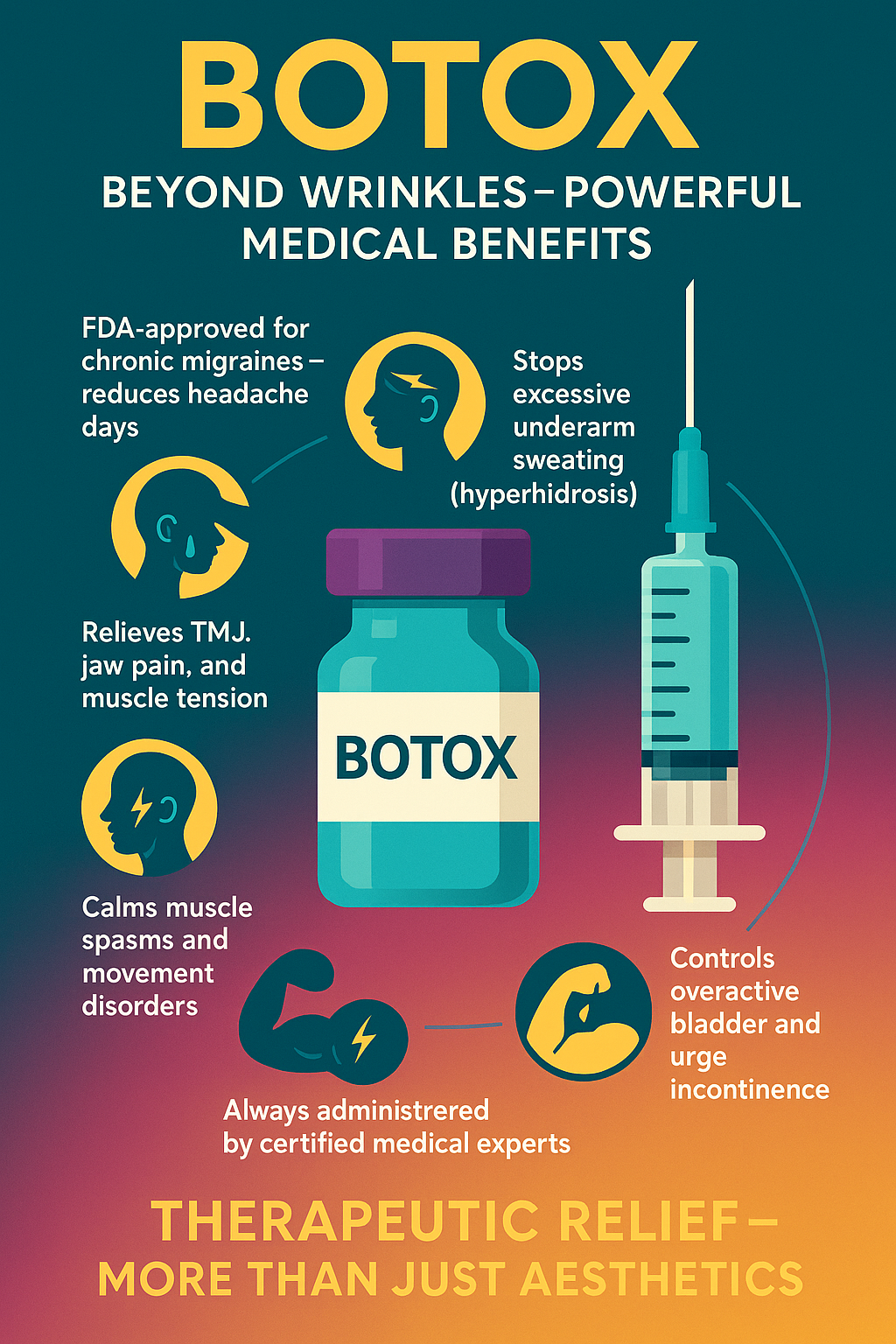
Botox® (onabotulinumtoxinA) is widely recognized for its ability to smooth facial wrinkles, but its therapeutic applications extend far beyond aesthetics. As a neuromodulator, Botox is FDA-approved and clinically validated for a range of medical conditions involving muscle overactivity, nerve signaling, and glandular dysfunction. At Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa, all therapeutic Botox treatments are performed by certified expert injectors under the direct supervision of Dr. Sherly Soleiman, MD, a board-certified physician and national trainer in advanced neuromodulator techniques.
Botox for Chronic Migraine
FDA Approval and Indication
Botox received FDA approval for chronic migraine prevention in 2010, following the PREEMPT clinical trials (PREEMPT 1 & 2, NCT00156910 and NCT00168428). It is indicated for adults experiencing 15 or more headache days per month, each lasting four hours or longer. FDA label
Mechanism of Action
Botox is injected into specific head and neck muscles to inhibit the release of pain-associated neurotransmitters, reducing migraine frequency and severity.
Treatment Protocol
Certified injectors administer a series of injections across 7 key muscle groups every 12 weeks. Individual results may vary.
Learn more about Botox for Migraines
Botox for Hyperhidrosis (Excessive Sweating)
FDA Approval and Indication
Botox was FDA-approved in 2004 for severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm sweating) unresponsive to topical agents. FDA label
Mechanism of Action
Botox blocks acetylcholine release at sweat glands, temporarily reducing sweat production.
Treatment Protocol
Multiple small injections are placed in the affected area (most commonly underarms). Effects typically last 4–6 months.
Learn more about Botox for Underarm Sweating
Botox for TMJ Disorders and Jaw Pain
Indication and Evidence
Botox is used off-label to treat temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction, jaw pain, and bruxism (teeth grinding). Clinical studies support its efficacy in reducing muscle hyperactivity and related pain (see Al-Wayli, 2017, J Oral Maxillofac Surg).
Mechanism of Action
Targeted injections relax the masseter and temporalis muscles, alleviating tension, pain, and jaw clenching.
Treatment Protocol
Administered by certified injectors, typically every 3–6 months, with dosing tailored to individual muscle mass and severity.
Learn more about Botox for TMJ
Botox for Muscle Spasticity and Dystonia
FDA Approval and Indication
Botox is FDA-approved for upper limb spasticity (2010), lower limb spasticity (2015), cervical dystonia (2000), and blepharospasm (1989). FDA label
Mechanism of Action
Botox interrupts abnormal nerve signaling to overactive muscles, reducing involuntary contractions and improving mobility.
Common Conditions Treated
- Cervical dystonia (neck muscle spasms)
- Blepharospasm (eyelid twitching)
- Hemifacial spasm
- Limb spasticity post-stroke or neurological injury
Botox for Overactive Bladder
FDA Approval and Indication
Botox was FDA-approved in 2011 for overactive bladder with symptoms of urge incontinence, urgency, and frequency in adults unresponsive to anticholinergic medications. FDA label
Mechanism of Action
Botox is injected into the bladder wall to relax detrusor muscles, increasing bladder capacity and reducing incontinence episodes.
Note
This procedure is typically performed by urologists or gynecologists.
Botox for Chronic Pain Syndromes
Off-Label Indications
Botox is used off-label for several pain conditions, including:
- Myofascial pain syndrome
- Plantar fasciitis (Botox for Plantar Fasciitis)
- Tennis elbow (Botox for Tennis Elbow)
- Neuropathic pain
Mechanism of Action
Botox inhibits pain neurotransmitter release and reduces muscle spasm, providing relief in select chronic pain syndromes.
Botox for Sialorrhea (Excessive Salivation)
FDA Approval and Indication
Botox was FDA-approved in 2018 for chronic sialorrhea (excessive drooling) in adults. FDA label
Mechanism of Action
Injected into salivary glands, Botox reduces saliva production by blocking acetylcholine release.
Botox for Facial Twitching and Hemifacial Spasm
Indication and Evidence
Botox is FDA-approved for blepharospasm and is widely used off-label for hemifacial spasm and other focal dystonias.
Mechanism of Action
Targeted injections relax overactive facial muscles, reducing involuntary movements.
Botox for Other Unique Medical Uses
- Raynaud’s phenomenon: Off-label use to reduce vasospasm in fingers and toes.
- Depression: Investigational studies suggest potential benefit, but not FDA-approved.
- Esophageal achalasia: Used in gastroenterology for select cases.
Why Expertise Matters: Safety and Results
Therapeutic Botox requires precise anatomical knowledge and advanced injection technique. At Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa, all treatments are performed by certified expert injectors under the direct supervision of Dr. Sherly Soleiman, MD, a board-certified physician and national faculty trainer for Allergan. Dr. Soleiman’s team follows rigorous protocols for patient safety, informed consent, and natural, effective outcomes.
“Patient safety and natural results are always our top priorities. Every patient receives a thorough medical evaluation and a customized treatment plan.” – Dr. Soleiman
Related Services at Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa
- Botox for Migraines
- Botox for TMJ
- Botox for Underarm Sweating
- Botox for Tennis Elbow
- Botox for Plantar Fasciitis
- Wrinkle Relaxers
Frequently Asked Questions
For more information or to schedule a consultation, contact Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa in Sherman Oaks, serving Los Angeles, Encino, Studio City, and Beverly Hills. All procedures are performed by certified experts under the direct supervision of Dr. Sherly Soleiman, MD, a national leader in medical aesthetics and neuromodulator therapy.
