Exosomes and bioceramic fillers represent a significant advancement in regenerative and aesthetic medicine, offering new possibilities for tissue repair, skin rejuvenation, and facial contouring. Exosomes—cell-derived vesicles—deliver bioactive signals that support cellular renewal, while bioceramic fillers such as calcium hydroxylapatite provide a stable scaffold for tissue integration and volumization. Recent clinical studies highlight the synergistic effects of combining these biomaterials, with promising results for both safety and efficacy in nonsurgical procedures. At Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa, all treatments are performed by certified experts under the direct supervision of Dr. Sherly Soleiman, MD, a board-certified physician and national leader in medical aesthetics.
The Science of Exosome and Bioceramic Injectable Fillers
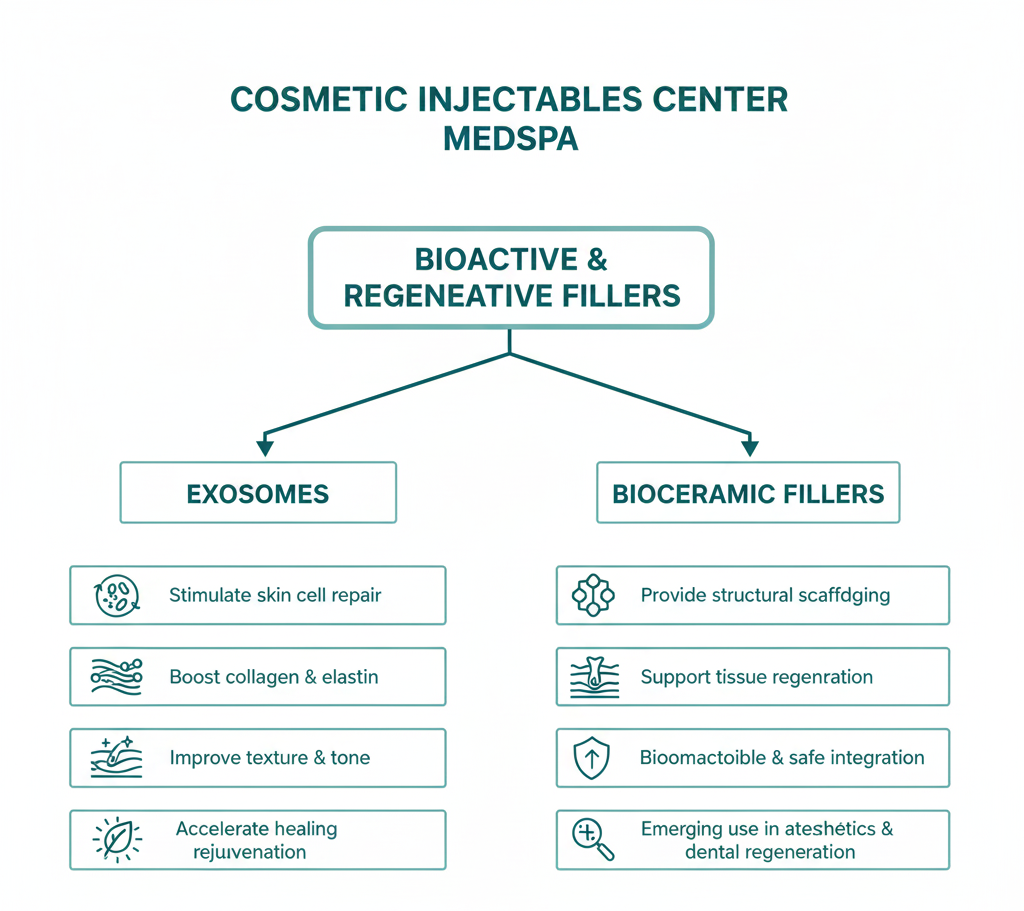
Exosome-bioceramic fillers represent a new class of injectable biomaterials designed for both regenerative and aesthetic medicine. Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells, carrying proteins, RNAs, and growth factors that modulate tissue repair and cellular communication. Bioceramic fillers, such as calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA), bioactive glass, and calcium silicates, provide a scaffold for tissue integration and sustained release of bioactive molecules.
Recent studies demonstrate that combining exosomes with bioceramic scaffolds or fillers can accelerate tissue regeneration, stimulate collagen and elastin production, and improve angiogenesis. These advances are supported by preclinical and early clinical data, with ongoing research into safety and efficacy for aesthetic applications (Acta Biomaterialia, 2025; Bioactive Materials, 2024). Dr. Sherly Soleiman, MD, a board-certified physician and national trainer in medical aesthetics, leads a team of certified experts at Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa, ensuring all procedures are grounded in the latest scientific evidence and performed under strict medical oversight.
Mechanisms: How Exosome-Bioceramic Fillers Work
Exosome Function in Regeneration
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or mineralized osteoblasts deliver microRNAs, growth factors, and proteins that drive cellular proliferation, migration, and differentiation. In aesthetic medicine, these properties are harnessed to stimulate neocollagenesis, elastin synthesis, and vascularization, supporting tissue rejuvenation and repair (Frontiers in Bioengineering, 2022).
Bioceramic Fillers as Scaffolds
Bioceramic fillers, including CaHA (e.g., Radiesse), bioactive glass, and calcium silicates, act as biocompatible scaffolds. They provide mechanical support, promote cell adhesion, and gradually resorb as new tissue forms. When combined with exosomes, these fillers serve as delivery vehicles, prolonging the bioactivity of exosomes and enhancing tissue integration (PMC/NIH, 2024).
Synergy: Exosome-Bioceramic Hybrids
Histological studies confirm that exosome-loaded bioceramic fillers increase dermal thickness, collagen deposition, and angiogenesis compared to fillers alone. In animal models, these hybrids accelerate bone and soft tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and improve vascularization (Acta Biomaterialia, 2025; Bioactive Materials, 2024).
Clinical Evidence and Current Applications
Preclinical and Early Clinical Studies
- Bone Regeneration: Exosome-bioceramic scaffolds have shown superior osteogenesis and angiogenesis in animal models, with upregulation of key genes (RUNX2, VEGF) and improved bone defect repair (PMC/NIH, 2025).
- Soft Tissue Aesthetics: Human split-face studies using exosomes with CaHA fillers demonstrate increased dermal thickness, neocollagenesis, and improved skin texture without major adverse events (Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 2023).
- Wound Healing: Pilot clinical trials report faster closure and reduced scarring in chronic wounds using exosome-bioceramic hybrids (Frontiers in Bioengineering, 2022).
Regulatory Status
Exosome-based injectables are classified as advanced therapeutics by the FDA, EMA, and MHRA. Current guidelines require rigorous quality control, purity, and safety testing. No exosome-bioceramic filler has full FDA approval for aesthetic use as of 2025, but several are in preclinical and early-phase clinical trials (PMC/NIH, 2025; ResearchGate, 2025). The FDA mandates Investigational New Drug (IND) applications for clinical studies, and the UK MHRA restricts unapproved exosome injections.
Procedure Options and Related Treatments
Exosome-Bioceramic Filler Types
| Filler Type | Bioceramic Component | Exosome Source | Clinical Status | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaHA + Exosomes | Calcium hydroxylapatite | MSC/Placental | Early clinical | Collagen stimulation, dermal thickening |
| Bioactive Glass + Exosomes | Mesoporous bioactive glass | MSC | Preclinical | Bone/soft tissue regeneration |
| Calcium Silicate + Exosomes | Lithium calcium silicate | MSC | Preclinical | Pro-angiogenic, collagen deposition |
Comparison Table: Exosome-Bioceramic Fillers vs. Established Fillers
| Feature/Property | Exosome-Bioceramic Fillers | Hyaluronic Acid Fillers | CaHA (Radiesse) | Sculptra (PLLA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Mechanism | Regeneration, biostimulation | Volume, hydration | Collagen stimulation | Collagen stimulation |
| Longevity (estimated) | 12-24 months* | 6-12 months | 12-18 months | 18-24 months |
| FDA Approval (2025) | No (in trials) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Tissue Integration | High (preclinical) | Moderate | High | High |
| Collagen/Elastin Boost | Yes (histological) | Mild | Yes | Yes |
| Inflammatory Risk | Low (early data) | Low | Low | Low |
| Use in Bone/Cartilage | Yes (preclinical) | No | Limited | No |
| Use in Soft Tissue | Yes (early clinical) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
*Longevity based on animal and early clinical data; individual results may vary.
Related Procedures at Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa
- Radiesse (CaHA) Fillers
- Sculptra (PLLA) Fillers
- PRP, PRF & Exosomes
- Morpheus8
- PDO Threads
- Microneedling
- Hyaluronic Acid Fillers
Safety, Patient Selection, and Clinical Considerations
Exosome-bioceramic fillers are generally well-tolerated in preclinical and early clinical studies, with no major adverse events reported. Key safety concerns include exosome purity, immunogenicity, and batch consistency. Regulatory agencies require strict quality controls and GMP manufacturing standards (PMC/NIH, 2025). Patient selection should prioritize those seeking regenerative outcomes, such as improved skin texture, dermal thickening, or bone/tissue repair.
At Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa, all procedures are performed by certified expert injectors under the direct supervision of Dr. Soleiman. Every patient receives a comprehensive Good Faith Exam, and all treatments are tailored to individual needs, with a focus on natural, proportional results.
Future Directions and Clinical Translation
Ongoing research is focused on optimizing exosome sourcing, bioceramic scaffold design, and delivery systems for injectable use. Phase I/II clinical trials are underway for both bone and soft tissue applications. Regulatory pathways are evolving, with the FDA and EMA emphasizing risk-based oversight and the need for standardized manufacturing. As these therapies progress, they may offer new options for patients seeking advanced regenerative and aesthetic outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Sherly Soleiman, MD, board-certified physician and national trainer in nonsurgical medical aesthetics at Cosmetic Injectables Center Medspa, Sherman Oaks, CA.
