Lip augmentation remains a leading medical aesthetic procedure, driven by evolving patient preferences and continuous innovation in both nonsurgical and surgical techniques. A 2024 scoping review published in the Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery comprehensively analyzed recent advancements, focusing on novel methods, efficacy, and safety in lip enhancement (Jain et al., 2024).
Overview of the Review
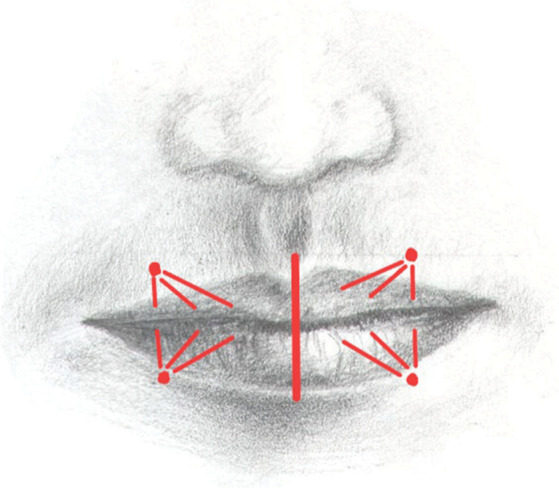
The review systematically evaluated literature from January 2013 to June 2023, identifying 16 eligible studies (9 nonsurgical, 7 surgical) that described new techniques for lip augmentation. Only studies with at least 10 patients, clear technique descriptions, and quantitative outcome reporting were included.
Nonsurgical Lip Augmentation: Injectable Filler Techniques
Injectable dermal fillers, particularly hyaluronic acid (HA) products, are currently the most frequently utilized approach for lip enhancement. The review highlighted several innovative techniques and products:
Key Techniques and Findings
- Four-Point Injection Technique (Sahan & Tamer): Utilizes four entry points per lip, administering HA filler (Juvéderm Ultra 4) with a fanning technique. In a cohort of 50 patients, 90% reported high satisfaction; no serious complications were observed.
- Bi-Bi Technique (Stéphane et al.): Combines intramuscular and dermal injections using both cannula and needle with two HA fillers. Patient satisfaction was high, with only minor post-treatment bruising and edema reported.
- Step-by-Step Φ (Phi) Technique (Keramidas et al.): Applies the golden ratio for injection points, limiting filler volume per session. Among 833 patients, most required three sessions for optimal results. Adverse effects were minor and self-limiting; no severe complications occurred.
- French Kiss Technique (Trévidic & Criollo-Lamilla): Focuses on lip eversion by everting the vermilion border. Ninety percent of patients rated their appearance as improved, with low pain and no major complications.
- LOVE Approach (Bertossi et al.): Employs a modular strategy for shaping, volumizing, and hydrating lips using different HA filler types (Vycross range). High satisfaction rates were noted, with transient edema and bruising as the most common side effects.
- Inverted Mercedes Benz Sign Technique (Adel): Utilizes three entry points for upper and lower lip injection. All patients reported high satisfaction, with only mild, temporary side effects.
- No-Touch Technique (Surek et al.): Avoids mucosal penetration, instead injecting from outside the white roll. This method minimized adverse events, with only minor, self-resolving injection-related reactions.
- Other Fillers and Techniques: The review also included studies using PMMA/collagen (Bellafill) and injectable platelet-rich fibrin (i-PRF+), with generally high satisfaction but shorter duration of effect for platelet-rich products.

Comparative Efficacy and Safety
- Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: No single HA product demonstrated clear superiority across all outcome measures. A recent head-to-head trial found minor differences in longevity and patient appraisal among Juvéderm, Belotero, Restylane, and Stylage, but safety profiles were similar and all products were well-tolerated (Steenen et al., 2023).
- Adverse Effects: The most common complications with fillers were mild erythema, swelling, and bruising, all of which were temporary. Serious complications (vascular occlusion, necrosis) were not observed in the reviewed studies.
Standardization Efforts
The review noted the emergence of standardized injection protocols, including the MD Codes™ system, which maps anatomical zones, suggests dosing, and highlights danger areas to improve safety and consistency among injectors.
Surgical Lip Augmentation Techniques
Surgical options, though less commonly performed than injectable procedures, were also reviewed:
- Subnasal Lip Lift (Bull’s Horn Excision): Multiple studies reported improved upper lip aesthetics and high patient satisfaction. Complications included scarring (1–10.5%), transient sensory changes, and rare need for revision.
- Modified Upper Lip Lift: Incorporates deep-plane release and fascial suspension for enhanced lift; most patients maintained normal movement and smile postoperatively.
- Microfat Grafting and Autogenous Fillers: Fat grafts and post-auricular fibroareolar tissue were used for volume restoration, with variable longevity and generally favorable outcomes.
- Endonasal Lift and Short Scar Techniques: Provided aesthetic improvements with low rates of infection or wound complications.
Comparative Outcomes
- Longevity: Surgical techniques offer more permanent results compared to fillers, but are associated with risks of scarring and longer recovery.
- Complication Profiles: While generally safe, surgical methods carry a higher risk of adverse scarring and sensory changes compared to injectable approaches.
Limitations and Recommendations
The review emphasized that most included studies were limited by small sample sizes, lack of standardized outcome measures, and low levels of evidence. The authors called for prospective, comparative studies to better define the relative benefits, risks, and patient selection criteria for both surgical and nonsurgical options.
Conclusions
- Injectable HA fillers remain the most popular method for lip augmentation, offering excellent but temporary results with a strong safety profile.
- Surgical techniques provide durable enhancement but have higher risks of scarring and sensory changes.
- Technique selection should be individualized, considering patient anatomy, desired outcomes, and risk tolerance.
- Standardization of injection protocols (e.g., MD Codes™) may improve safety and consistency.
- Future research should prioritize high-quality, comparative studies to further clarify best practices.
For a detailed review and full references, see the original article: Advancements in lip augmentation: A scoping review exploring novel techniques, J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2024.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most recent advancements in lip augmentation?
Recent advancements include novel injection techniques (e.g., Four-Point, Bi-Bi, Step-by-Step Φ, French Kiss, LOVE approach, No-Touch) and new surgical modifications (e.g., deep-plane lip lifts, autogenous fillers). These methods aim to improve safety, precision, and patient satisfaction (Jain et al., 2024).
How do injectable fillers compare to surgical lip augmentation?
Injectable fillers, especially hyaluronic acid-based products, provide temporary but highly customizable results with a low risk of serious complications. Surgical techniques offer more permanent enhancement but are associated with higher rates of scarring and sensory changes.
Are certain hyaluronic acid fillers superior for lip augmentation?
Current evidence does not demonstrate clear superiority of any single HA filler. Minor differences in longevity and patient satisfaction exist, but all major brands have similar safety profiles (Steenen et al., 2023). Individual results may vary.
What are the most common complications of lip filler procedures?
The most common complications are mild and temporary, including erythema, swelling, and bruising. Serious adverse events such as vascular occlusion are rare when procedures are performed by experienced injectors.
What is the role of standardized injection protocols like MD Codes™?
Standardized protocols such as MD Codes™ help guide injectors on anatomical zones, dosing, and technique, improving consistency and minimizing risk.
How long do the results of lip fillers last?
Results from hyaluronic acid fillers are temporary, typically lasting several months depending on the product and individual metabolism. Surgical techniques offer more permanent results but involve greater recovery and risk.
Are there permanent filler options for lips?
Permanent fillers (e.g., PMMA/collagen) exist but are less commonly used due to higher risks of adverse events and complications. Most experts recommend temporary fillers for safety and reversibility.
What are the key factors for achieving natural-looking results?
A comprehensive understanding of lip anatomy, individualized technique selection, and conservative volume enhancement are critical for achieving natural, proportional outcomes.
Is there a risk of scarring with surgical lip augmentation?
Yes, surgical techniques carry a risk of visible scarring and sensory changes, though rates vary by method and patient factors. Non-surgical fillers do not cause scarring.
What further research is needed in lip augmentation?
High-quality, prospective studies comparing surgical and nonsurgical techniques, standardized outcome measures, and long-term safety data are needed to further guide best practices.
This summary is based on the findings of Jain R, Tanawde S, Joshi S, et al. “Advancements in lip augmentation: A scoping review exploring novel techniques.” J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2024;17(3):167–176. PMC11497539. Individual results may vary. This content is for educational purposes and not a substitute for professional medical advice.
